ASSESS THE LEVEL OF STRESS AMONG THE STAFF NURSE WORKING IN SAVEETHA MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL DURING COVID-19 PANDEMIC
Department of Medical Surgical Nursing, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India
*Corresponding Author:
Vishnu Priya V, Department of Medical Surgical Nursing, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai,
India,
Email: vishnupriya@saveetha.com
Received: 28-Sep-2022, Manuscript No. AJOPY-22-76163;
Editor assigned: 30-Sep-2022, Pre QC No. AJOPY-22-76163 (PQ);
Reviewed: 14-Oct-2022, QC No. AJOPY-22-76163;
Revised: 03-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. AJOPY-22-76163 (R);
Published:
10-Jan-2023, DOI: 10.54615/2231- 7805.47291
Abstract
Corona virus is a crucial respiratory disease, which impacted the health in both aspects, physically and mentally. High expectations, lack of time, skills, and social support may lead to occupational stress among nurses, which spontaneously causes anxiety, post traumatic stress disorder, distress, and other psychological problems. Nurses may also accompany with somatic symptoms, such as palpitations, nausea, dyspnea, and dizziness. The study aims to assess the level of stress among the nurses at SMCH and association between the level of stress and selected demographic variables of staff nurse in quantitative non experimental approach by descriptive research design. A samples was 50 staff nurse selected using recruited by non-probability purposive sampling technique. A selfstructured questionnaire and Likert 5 point scale was used to assess the demographic data and level of stress among the staff nurses. The results shows that, about 38 (76%) of the staff nurse had severe stress, 5 (10%) of the staff nurse had moderate stress and remaining 7 (14%) of the were of mild stress. The chi-square test also shows statistically significant association between education and level of stress among staff nurses at p<0.05 level. This study concluded that, the corona virus has caused severe stress among the nurses at SMCH. ASEAN Journal of Psychiatry, Vol. 24 (1) January, 2023; 1-6.
Keywords
Stress Level, SMCH, Chi-Square, Corona Virus, COVID 19 Pandemic
Introduction
Health of inhabitants is wobbling day by day. Healths furnish life, any commute in health that attributes to affliction. The world has experienced several pandemic of contagious disease, in past two decades, such as SAR in 2003, HIM, in 2009, Ebola zika and MERS in 2014-2016. The novel corona virus (COVID-19) pandemic has afforded, an unprecedented challenge to health care system across the world, which intern affects the nurses health, well-being and ability to work. The corona virus has accentuates the health care worker. A study among Jordanian health care workers, states that overall, mean score of fear of COVID-19 was 23.64 (SD+6.85). The nurses common risk factors are lack of effective hospital management system, reliable source and personal protective equipments, they act as major stressors among health care workers. High level of psychological stress has been recorded among nurses, by their concern service during COVID outbreak [1-3]. Frontline nursing staff and health care workers had suffered with severe anxiety and depression in early stages of epidemic, due to work pressure, insufficient financial support, lack of knowledge and lack of personal protective equipment, phobia due to increase mortality and morbidity of corona virus. Consequently nurses, have low efficacy about the nature of profession, thus further induces the stress, due to loss of patients and credit even with maximum effort and comprehensive care during pandemic crisis [4].
Objectives
• To assess the level of stress among the nurses at SMCH.
• To find association between the level of stress and selected demographic variables of staff nurse.
Materials and Methods
A quantitative approach with non-experimental research design was used to conduct the study in Saveetha medical college and hospital. 50 samples were selected by using a non-probability purposive sampling technique The criteria for sample selection staff nurses working in COVID 19 pandemic patients stress level assessing staff nurses who are working COVID 19 pandemic in Saveetha medical college and hospital willing to participate in the study. Exclusion criteria staff nurses who are not willing to participate in the study. Staff nurses those who not exposed to COVID wards. The data collection period was done with prior permission from the nursing head of department. The purpose of the study was explained to the samples and written informed consent was obtained from them. The data will collect from the questionnaires. 5 point stress assessing scale.
Results
Sample characteristics
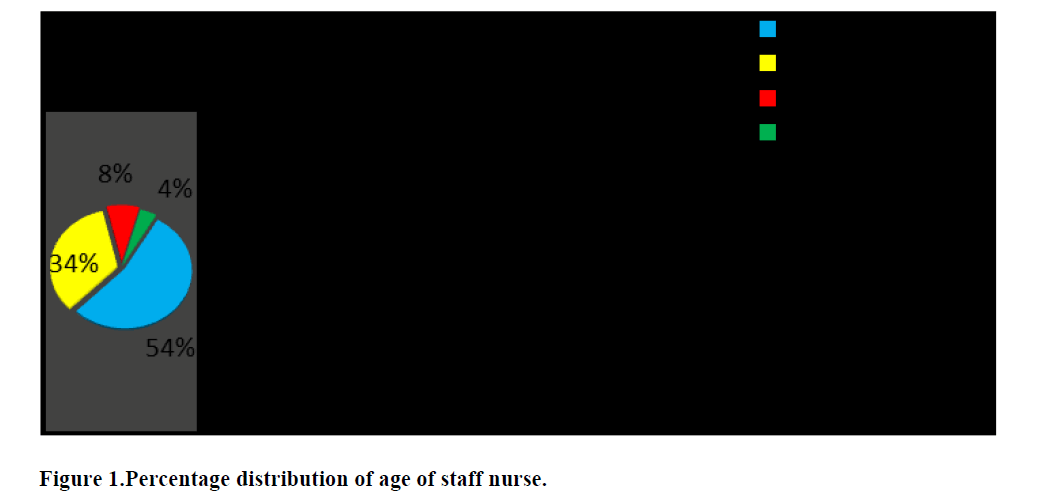
Among the selected staff nurses for 50 samples, most of the staff nurses that is 27 (54%) were in age group 20-25, 17 (34%) are belonging to the age group of 25-30, about 4 (8%) were of 30-35 group and 2 (4%) were above 35. Maximum 80% of the population were females and 20% were males. While assessing the religious factor, about 29 (58%) were Hindu, 19 (38%) were Christian and remaining 2 (4%) were Muslims. Education status is clear through the data that 24 of the staff nurse (48%) were perceived ANR and GNM nursing, 14 (28%) were of PBBS nursing and remaining, 12 (24%) were BSc nursing. While assessing the years of experience, 22 staff nurses (44%) were of 1-3 years, 23 staff nurse (46%) were 4-6 years and about 4 (8%) was of 7-10 years of experience (Figure 1).
The present study is supported by Randa M said, et al., conducted a study on occupational stress, john satisfaction and intent to leave nurses working in frontline during COVID-19 pandemic in amazing city, Egypt. The purpose of this study was to assess occupational stress, job satisfaction, and intent to leave among nurses dealing with suspected COVID-19 patients [5]. Assessment was done using online questionnaire formed of the expanded nursing stress scale, the McCloskey/Mueller satisfaction scale, and questionnaire assessing specific COVID-19 associated stressors and nurses intent to leave. Three quarters of nurses (75.2%) in ZFH had high stress level. Only 4.8% of nurses in ZFH definitely had no intent to leave their present job [6-8].
To assess the level of stress among the staff nurse working at Saveetha medical college and hospital
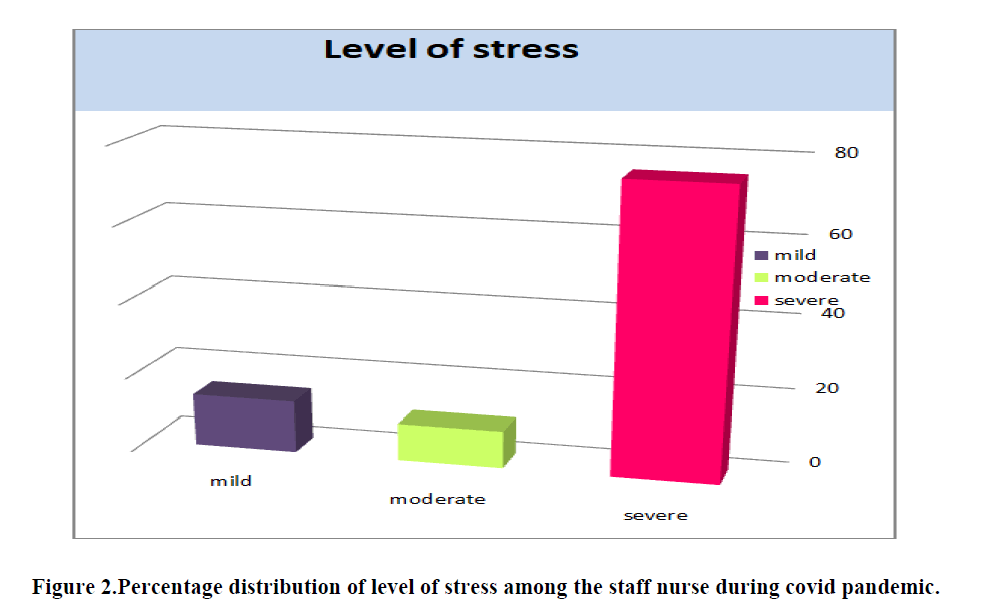
Table 1 shows that, about 38 (76%) of the staff nurse had severe stress, 5 (10%) of the staff nurse had moderate stress and remaining 7 (14%) were of mild stress (Figure 2).
Table 1. Frequency and percentage distribution of level of stress among nurses.
| Level of stress |
Frequency (f) |
Percentage % |
| Mild stress |
7 |
14 |
| Moderate stress |
5 |
10 |
| Severe stress |
38 |
76 |
The present study is supported by Mohammed god elbgury, et al., conducted a study on effect of COVID-19 stressors on health care workers, performance and attitude at Suez Canal university hospitals. This study was aims to assess effect of COVID-19 stressors on healthcare workers performance and attitude. Descriptive crosses sectional research design was used by convenient samples were collected. A total of 57.4% of the studied medical participants had moderate stress, while 49.1% of the paramedical participants had moderate COVID-19 psychological stress levels. But less than one quarter had severe, psychological stress levels. There is a significant correlation between COVID-19 psychological stressor levels and satisfactory level of knowledge among medical participants [9-15].
To find out the association between the levels of stress with the selected demographic variables of the staff nurse
The demographic variable education had shown statistically significant association with level of stress among staff nurses at p<0.05 level and the other demographic variables had not shown statistically significant association with level of stress among staff nurses [16-20].
Discussion
Our group has a wealth of research and knowledge, which has resulted in high quality publications (10), (11), (12), (13), (14), (15), (16), (17), (18), (19), (20), (21), (22), (23), (26). The present study encounters, about 76% of the study of the staff nurses had severe stress in SMCH, only 10% of them were of moderate stress and 14% of them were of mild stress [21-23].
Conclusion
This indicates that the study acts as easy method to assess the stress level among staff nurses working in COVID 19 pandemic in Saveetha medical college and hospital.
Acknowledgment
We would like to extend our gratitude to the authorities of Saveetha college of nursing, and staff nurses in Saveetha medical college and hospital.
Author's Contribution
All the authors actively participated in the work of the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Zhang Y, Wang C, Pan W, Zheng J, Gao J, et al. Stress, burnout, and coping strategies of frontline nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan and Shanghai, China. Front Psychiatry. 2020; 11:1154.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Arnetz JE, Goetz CM, Arnetz BB, Arble E. Nurse reports of stressful situations during the COVID-19 pandemic: Qualitative analysis of survey responses. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17(21):8126.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Alnazly E, Khraisat OM, Al-Bashaireh AM, Bryant CL. Anxiety, depression, stress, fear and social support during COVID-19 pandemic among Jordanian healthcare workers. Plos one. 2021; 16(3): 0247679.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Chowdhury SR, Sunna TC, Das DC, Kabir H, Hossain A, et al. Mental health symptoms among the nurses of Bangladesh during the COVID-19 pandemic. Middle East Curr Psychiatry. 2021; 28(1): 1-8.
[Crossref][Googlescholar]
- Tam CW, Pang EP, Lam LC, Chiu HF. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in Hong Kong in 2003: Stress and psychological impact among frontline healthcare workers. Psychol Med. 2004; 34(7):1197-1204.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Zhang C, Yang L, Liu S, Ma S, Wang Y, et al. Survey of insomnia and related social psychological factors among medical staff involved in the 2019 novel coronavirus disease outbreak. Front Psychiatry. 2020; 11:306.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Zhan YX, Zhao SY, Yuan J, Liu H, Liu YF, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors on fatigue of first line nurses combating with COVID-19 in China: A descriptive cross-sectional study. Curr Med Sci. 2020; 40(4):625-635.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Elbqry MG, Elmansy FM, Elsayed AE, Mansour B, Tantawy A, et al. Effect of COVID-19 stressors on healthcare workers’ performance and attitude at Suez Canal university hospitals. Middle East Curr Psychiatry. 2021; 28(1): 1-8.
[Crossref][Googlescholar]
- Salameh P, Aline HAJJ, Badro DA, Abou Selwan C, Randa AOUN, et al. Mental health outcomes of the COVID-19 pandemic and a collapsing economy: perspectives from a developingcountry. Psychiatry Res. 2020; 294:113520.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Prasad M, Rajagopal P, Devarajan N, Veeraraghavan VP, Palanisamy CP, et al. A comprehensive review on high fat diet-induced diabetes mellitus: An epigenetic view. J Nutr Biochem. 2022; 107: 109037.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Saravanakumar K, de Silv S, Santosh SS, Sathiyaseelan A, Ganeshalingam A, et al. Impact of industrial effluents on the environment and human health and their remediation using mofs-based hybrid membrane filtration techniques. Chemosphere. 2022; 307: 135593.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Babu S, Krishnan M, Priya Veeraraghavan V, Jayaraman S. Role of salivary mirnas in the diagnosis and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2022;132:105993.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Renu K, Veeraraghavan VP, Raj AT, Patil S, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A. The Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-alpha (PPAR-α): A new therapeutic target for oral cancer. OralOncol. 2022;132:106007.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Prasad M, Jayaraman S, Veeraraghavan VP. An intriguing role of circular RNA in insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: the future perspectives. Hypertens Res. 2022; 45(11):1843-1845.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Kullappan M, Benedict BA, Rajajagadeesan A, Baskaran P, Periadurai ND, et al. Ellagic Acid as a Potential Inhibitor against the Nonstructural Protein NS3 Helicase of Zika Virus: A Molecular Modelling Study. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2044577.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Mony U, Veeraraghavan VP. Cerenkov luminescence imaging: A future nuclear imaging modality of head and neck oncology patients in low income countries? Oral Oncol. 2022; 130:105923.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Pazhani J, Jayaraman S, Veeraraghavan VP, Somasundaram DB, Raj AT, et al. Targeting cancer associated fibroblasts-A TGF-β based immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2022; 130:105899.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Pei J, Umapathy VR, Vengadassalapathy S, Hussain SFJ, Rajagopal P, et al. A Review of the Potential Consequences of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum glaucum) for Diabetes Mellitus and Other Biomedical Applications. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2932.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Sujatha G, Veeraraghavan VP, Alamoudi A, Bahammam MA, Bahammam SA, et al. Role of Toothbrushes as Gene Expression Profiling Tool for Oral Cancer Screening in Tobacco and Alcohol Users. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(13):8052.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]
- Hu A, Alarfaj AA, Hirad AH, Veeraraghavan VP, Surapaneni KM, et al. Chitosan-sodium alginate-polyethylene glycol-crocin nanocomposite treatment inhibits esophageal cancer KYSE-150 cell growth via inducing apoptotic cell death. Arab J Chem. 2022; 15(6): 103844.
[Crossref][Googlescholar]
- Wei W, Li R, Liu Q, Seshadri VD, Veeraraghavan VP,et al. Amelioration of oxidative stress, inflammation and tumor promotion by Tin oxide-Sodium alginate-Polyethylene glycol-Allyl isothiocyanate nanocomposites on the 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. Arab J Chem. 2021; 14(8):103238.
[Crossref][Googlescholar]
- Zhao Y, Dang M, Zhang W, Lei Y, Ramesh Tet al. Neuroprotective effects of Syringic acid against aluminium chloride induced oxidative stress mediated neuroinflammation in rat model of Alzheimer's disease. J Funct Foods. 2020;71:104009.
[Crossref][Googlescholar]
- Mony U, Priya Veeraraghavan V. "Rules" to the genetic progression of tumours deciphered: Is it time to think differently in treating oral cancer patients? Oral Oncol. 2022;134:106111.
[Crossref][Googlescholar][Pubmed]